Coxarthrosis of the hip joint is a complex process of degenerative-dystrophic nature.The disease has a fairly wide clinical spectrum and is mainly characterized in people over 40 years of age, however, it can also be diagnosed at younger ages, especially in children and adolescents.
Most often, the precursors to the development of coxarthrosis in the hip joint are various types of injuries and inflammations, the treatment of which is absent or incomplete.
There are several levels of development of the degenerative-dystrophic process, each of which requires a specific direction of complex treatment methods.
What is coxarthrosis of the hip joint?
Coxarthrosis or osteoarthritis/deformity of the hip joint is a complex pathology of the largest joint of the human body, accompanied by the gradual destruction of bone and cartilage tissue.The development process is gradual.
Late diagnosis as well as lack of appropriate treatment will cause deformation of adjacent bone surfaces and the appearance of bone growth on them, limiting mobility and hindering a person's normal life.
Statistics show that this type of disease occurs in 12% of cases of diagnosed pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Causes of coxarthrosis
Today, it is customary to distinguish two types of coxarthrosis of the hip joint:
- main, its appearance is inexplicable;
- secondary, developing against the background of other existing diseases.
With primary coxarthrosis, concomitant pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are often observed, including osteoarthritis in various parts of the spine.
Among the most probable reasons are the following:
- pathology of the development of the musculoskeletal system (dysplasia);
- Aseptic necrosis of joint tissue;
- infectious lesions;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- injury.
Risk factors
Among the factors that increase the risk of developing coxarthrosis in the hip joint, it is often emphasized:
- the load increases systematically;
- poor circulation in joint tissues;
- hormonal changes;
- metabolic disorders;
- natural aging;
- An active lifestyle is not enough.
It is worth noting that coxarthrosis itself cannot be inherited;Accordingly, people with such a diagnosis do not have a genetic predisposition to this disease;However, the manifestation of genetic factors can be considered other features of the body's activity that provoke the development of pathology.Features of this type include metabolic disorders, special structures of the musculoskeletal system, as well as weakness of joint tissues.
Degree of coxarthrosis
Degenerative-dystrophic diseases, like any other pathology, have degrees of development.Coxarthrosis has only three of them, each of which is characterized by the presence of certain changes.
Grade 1 coxarthrosis
With grade 1 coxarthrosis, there is a relatively moderate reduction in joint space, accompanied by the growth of bone tissue over the entire joint surface.
There were no pathological changes on the femoral surface.
Coxarthrosis grade 2
With level 2 coxarthrosis, the distance between the bones and joints is significantly narrowed, more than 50% lower than the generally accepted index.Pathological processes cause displacement of the femur, accompanied by deformation of the head, significantly increased in size and covered with numerous irregularities along the contour.
At this stage of development, bone growth occurs on all surfaces of the acetabulum, not limited to the cartilage.
Coxarthrosis grade 3
Grade 3 coxarthrosis is characterized by a pronounced deviation of functional indicators, as well as a sharp decrease in the distance between the bones of the joint.In addition, the femoral head also has obvious growth as well as many bones develop.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
The main and frequent symptom of the disease is pain of varying severity.The detailed symptomatic picture is determined by the intensity of development of pathological processes.
Grade 1 coxarthrosis involves the presence of symptoms such as:
- pain occurs systematically due to physical activity of varying intensity;
- Locate discomfort and pain in the hip/knee area.
Grade 2 coxarthrosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- moderate pain intensity, usually manifested at rest;
- pain spreading to the hip and groin area;
- the appearance of lameness after performing various types of exercises;
- reduced available range of motion (limited ability to abduct limbs to the side).
With coxarthrosis of the 3rd degree, the following symptoms are observed:
- constant, unbearable pain at any time of the day;
- the need to use a cane to move around;
- limited motor function, reduced muscle mass and shortened length of the lower limbs;
- body tilt.
Diagnosis of disease
The initial diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints, as well as the results of the visual examination and the medical history collected.
Diagnostic procedures to determine a disease such as coxarthrosis are aimed at identifying clinical signs and studying data from additional studies, which are mainly radiographic.
X-ray for coxarthrosis allows you to identify bypass pathological processes and determine the cause of their appearance.In particular, based on the X-ray results, the treating doctor can determine the injury.
Among other instrumental diagnostic methods, the following are used:
- CT (computed tomography) – allows you to create a detailed picture of the pathology;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - helps assess the extent of soft tissue damage.
It is also important to note the existence of a differential diagnosis, which includes the exclusion of pathological processes such as gonorrhea and osteoarthritis of the spine.
Laboratory tests are also an integral part of a complex diagnosis, including:
- General blood and urine tests to determine the patient's health status;
- biochemical blood tests to determine pathological conditions.
Treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
An orthopedic surgeon will make a diagnosis and determine a treatment plan.Treatment tactics are formed based on data such as:
- expression level;
- disease form;
- development reasons;
- presence of symptoms.
Today, there are several effective directions in the treatment of coxarthrosis.Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Physical therapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment of patients includes the appointment of procedures such as:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- shock wave therapy.
All used physiotherapy techniques help improve blood circulation, start metabolism and, of course, accelerate tissue regeneration.
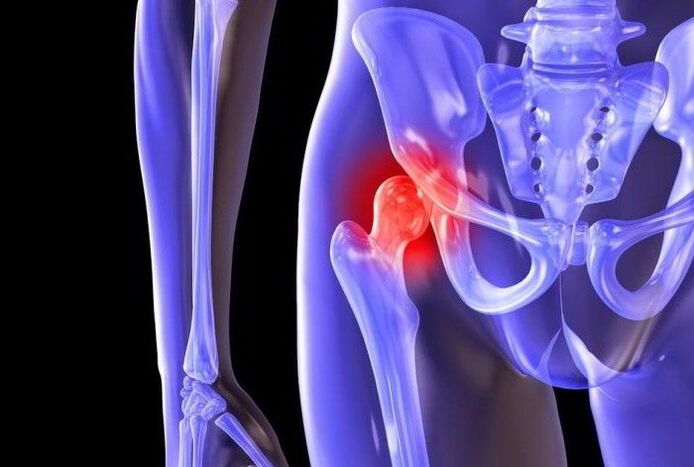
Drugs to treat coxarthrosis
Treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint with the help of drugs involves the use of such means as:
- muscle relaxants;
- NSAIDs;
- vasodilators;
- analgesic;
- corticosteroids;
- chondroprotector.
A group of drugs that are particularly important in the treatment of diseases are cartilage-protecting drugs that help promote tissue recovery.
Exercise therapy (physical therapy)
Therapeutic physical education classes are one of the most effective methods of complex treatment.
A set of exercises developed by a medical professional based on the patient's diagnosis and existing physical level.
Massage
Treatment of coxarthrosis involves the use of various types of massage:
- classic;
- point;
- vacuum.
In the absence of contraindications, after just a few treatment sessions, the patient will see improved blood circulation in the joint area and the supply of nutrients required by the tissues will be replenished.
Participate in massage sessions that help strengthen and restore the soft tissues of the joints.
Surgical intervention for coxarthrosis
The ineffectiveness of conservative treatment forces people to resort to radical pathological methods.
Steady progression of pathological processes is a direct indication for surgical intervention.Today, there are two types of surgery performed:
- arthroplasty – removes the femoral head from the acetabulum and then corrects changes in joint tissue;
- endoscopy – implant installation.
Surgery is performed when the patient's pathological condition is at level 3, meaning that destructive changes in joint tissue cannot be eliminated.
Prognosis and possible complications
Only stage 1 degenerative-dystrophy can be successfully treated conservatively.In other cases, it is impossible to talk about complete restoration of functional activity of the hip joint, except in cases of prosthetic installation.
In the absence of treatment, at the final stage of development of the pathological process, the patient has limited mobility of the flexion-type joints, which prevents the patient from moving due to the constant bending of the limb.
After complete fusion, the patient cannot solve basic daily problems on his own and is considered disabled.
preventive measures
Preventive measures can be used to prevent the occurrence of pathological processes, as well as during remission, prevent progression of the disease.
Prevention of coxarthrosis includes:
- maintain a balanced diet;
- systematic sports;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle, including giving up bad habits;
- control body weight;
- Systematic preventive examination and timely treatment of various diseases.
Remember that your health is only in your hands.Keep him in optimal condition and enjoy a full life!

























